Object.create()
语法
create(o: object | null, properties: PropertyDescriptorMap & ThisType<any>): any;
描述
用于创建一个新的对象,它使用现有对象作为新对象的 __proto__.
第一个参数为原型对象
第二个参数可选,即给这个新对象配置属性描述符,这些属性对应着 Object.defineProperties() 的第二个参数,如果此参数不是 null 或对象,将会报错
示例
继承一个普通对象,第二个参数是一个属性描述符的对象。
const cat = {
name: null,
color: 'white',
say() {
return `I'm ${this.name}`;
},
};
// 若有第二个参数,必须是 null 或一个对象
// TypeError: Property description must be an object: a
// Object.create(cat, 'abc');
const kitty = Object.create(cat, {
name: {
value: 'Kitty',
writable: false,
enumerable: true,
configurable: false,
},
color: {
value: 'pink',
writable: false,
enumerable: true,
configurable: false,
},
});
Object.getOwnPropertyDescriptors(kitty);
// 输出如下
{ name:
{ value: 'Kitty',
writable: false,
enumerable: true,
configurable: false },
color:
{ value: 'pink',
writable: false,
enumerable: true,
configurable: false } }
传统来讲我们通过下面的方法实现类的继承。
function Animal(name) {
this.name = name;
}
Animal.prototype.say = function() {
return `I'm ${this.name}`;
};
function Cat(name) {
// 继承属性
Animal.call(this, name);
}
// 继承方法
Cat.prototype = new Animal();
当使用 Object.create() 后子类的继承可以写成这样。
function Cat() {
Animal.call(this);
}
Cat.prototype = Object.create(Animal.prototype);
Cat.prototype.constructor = Cat;
扩展
Object.create() 和 new 的区别
我们回忆一下 new 的实现过程:
创建一个空对象
将构造器函数的原型赋值给此空对象
将构造器函数的 this 指向创建的空对象
var o = new Object();
o.__proto__ = A.prototype;
A.call(o);
然后我们看一下 MDN 上关于 Object.create() 的 polyfill,为了简单这里不贴关于第二个参数的逻辑。可以看到它是先创建一个空函数 F,然后将参数设置为 F 的原型,最后返回 F 的实例。
if (typeof Object.create !== "function") {
Object.create = function(proto, propertiesObject) {
if (typeof proto !== "object" && typeof proto !== "function") {
throw new TypeError("Object prototype may only be an Object: " + proto);
} else if (proto === null) {
throw new Error(
"This browser's implementation of Object.create is a shim and doesn't support 'null' as the first argument."
);
}
if (typeof propertiesObject != "undefined")
throw new Error(
"This browser's implementation of Object.create is a shim and doesn't support a second argument."
);
//实现一个隐藏函数
function F() {}
//函数的原型设置为参数传进来的原型
F.prototype = proto;
// 返回一个F函数的实例,即此实例的__proto__指向为参数proto
return new F();
};
}
所以 new 后面跟的是构造函数,而 Object.create() 后面跟的是原型。
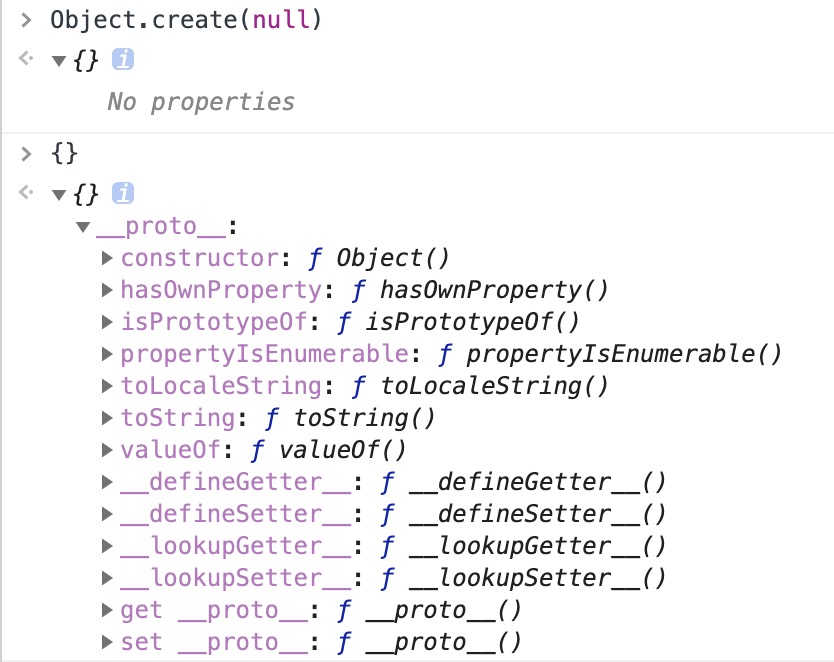
Object.create(null)
因为 null 是原型链的终点,因此以 null 为 __proto__ 创建的空对象是一个完全纯净的对象,看下图便一目了然。